

Here is a table from the Kotlin in Action book that summarises these modifiers. You can only create an extension function of a public class Summary With private declarations are only visible in the class as in Java but in Kotlin also in the file (top level declarations) where it is declared.Īnother difference is that in Kotlin outer classes do not see private nested (or inner) classes protectedĭeclarations are only visible in its class and in its subclassess Note: Extension FunctionsĮxtension functions don’t get access to its private or protected members. External code can define classes in the package you are trying to protect. Internal provides real encapsulation for the implementation details, while in Java’s package-private encapsulation could be broken. modules can be: maven projects, gradle sets, files generated from an Ant task, or a IntelliJ IDEA module
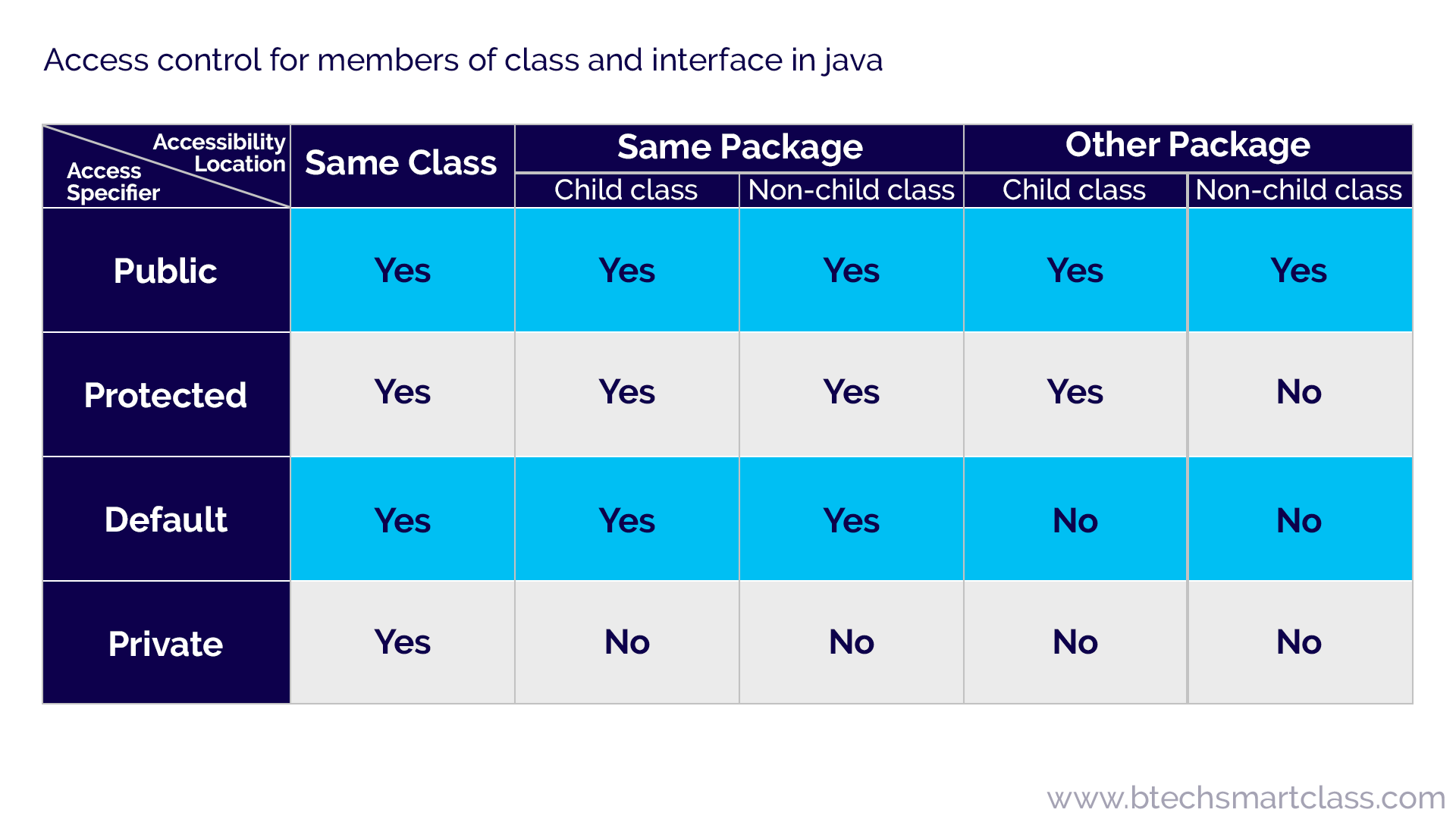
internal means that the declarations are visible inside a module.Ī module in kotlin is a set of Kotlin files compiled together. Internal is an alternative to Java’s package-private. Java also has a fourth visibility modifier, package-private, which is also a default visibility modifier (if you dont specify a visibility modifier, then. In Kotlin the default visibility modifier is public while in Java is package-private. The public modifiers means that the declarations are visible everywhere. Visibility modifiers control which declarations are visible from others. “Man on a safari expedition looking through binoculars” by Louis Blythe on Unsplash


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
